About Crystalline Arthropathies: Gout and CPPD
- Gout monosodium urate (MSU) crystal deposition
- Male predominance
- Most common inflammatory arthritis for older males
- Peak onset: 40-60 yo
- Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD): CPP crystal deposition
- Previously referred to as pseudogout
- Disease of elderly, onset >50 yo
- Likes damaged joints
- Female predominance
- Basic calcium phosphate (BCP): BCP crystal deposition
- Predilection for shoulder
Gout
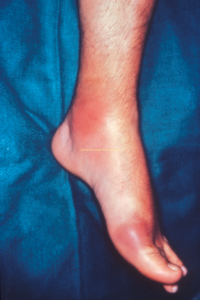
- Inflammatory arthritis: most common presentation in 1st MTP (podagra) but may affect any joint or bursa; does not involve the axial spine
- Abrupt onset: severe joint pain & swelling (view image)
- Triggers and risk factors: beer, other alcohol, red meat, seafood, high fructose drinks, kidney injury/fluid shifts
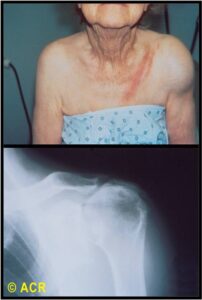
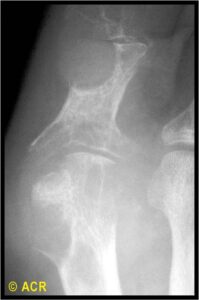
Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (CPPD)
- Chronic: crystal deposition without flare
- Acute flare: acute, severe arthritis
- Most common joints involved: knee, wrist, 1st and 2nd MCPs
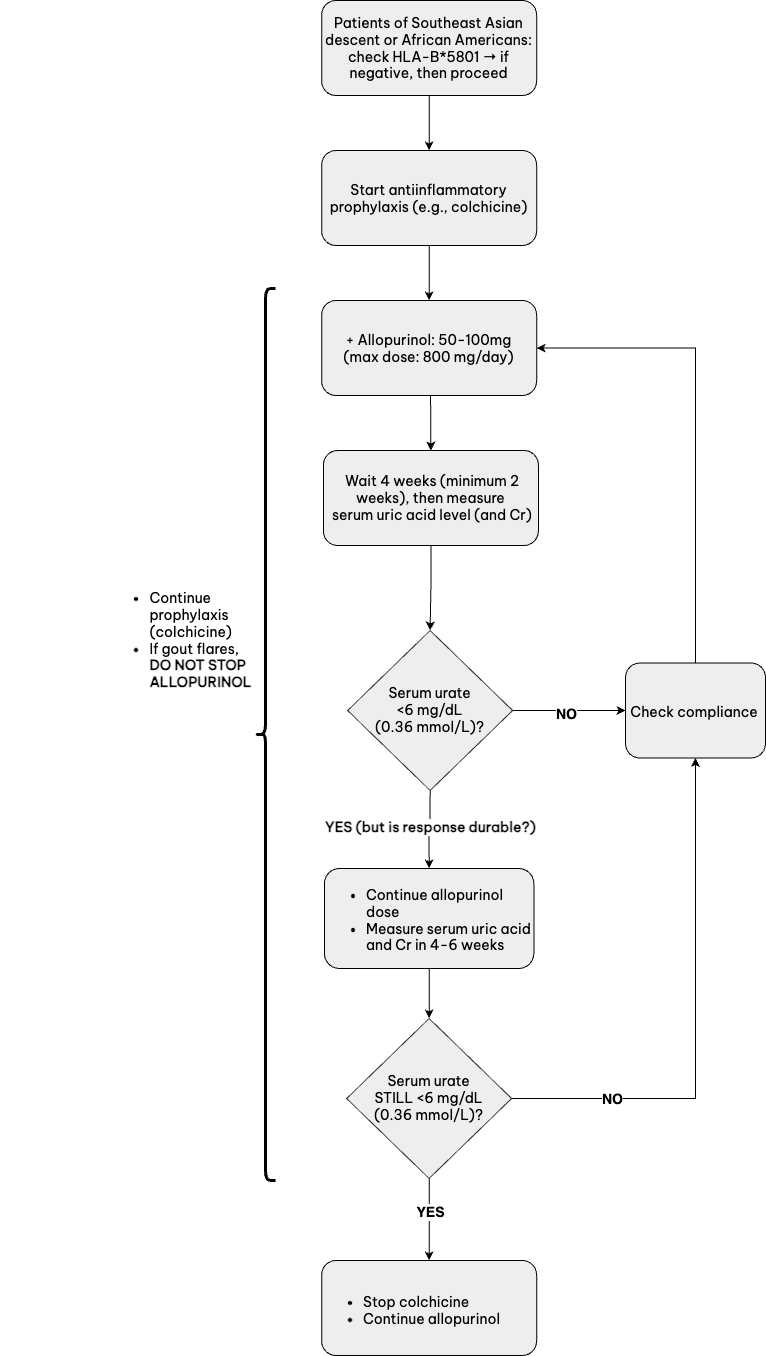
BCP Arthritis
- Most common: acute calcific arthritis and periarthritis of the shoulder (view image)
Arthrocentesis
- Gold standard for diagnosis of crystalline arthropathies
- Synovial fluid analysis: crystals, cell count+diff, Gram stain, culture
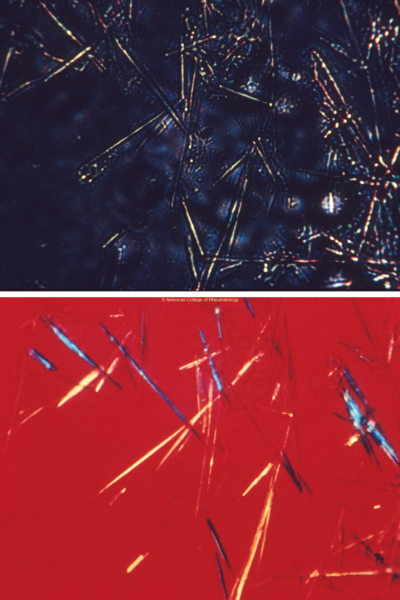
Polarized Microscopy
- MSU crystals (view image):
- Needle shaped
- Negatively birefringent
- CPP crystals:
- Rhomboid shaped
- Positively birefringent
- Special calcium staining needed to identify BCP crystals
Labs
Imaging
- Radiographs
- MSK ultrasound
- Dual-energy CT
-
Infection/septic joint
-
Other etiologies for inflammatory arthropathy
-
Hemochromatosis can present like CPPD
Other Rheumatologic Disease
Endocrinopathy
- Thyroid disease
- Hemochromatosis
Acute Flare Reduction
- NSAIDs
- Colchicine
- Glucocorticoids
- IL-1 axis inhibitors:
- Anakinra: 100 mg subcutaneously once daily for 3-5 days
- Canakinumab: single 150 mg subcutaneous dose
- Intra-articular steroids
- Systemic glucocorticoids
Long-Term Treatment
Goal: Flare prevention
CPPD
- Colchicine
- Consider DMARDs like hydroxychloroquine
Gout
- Dietary and lifestyle modifications: low purine diet, weight loss, etc.
- Serum uric acid <6 mg/dL or lower for tophaceous +/- erosive disease
- Urate-lowering therapies:
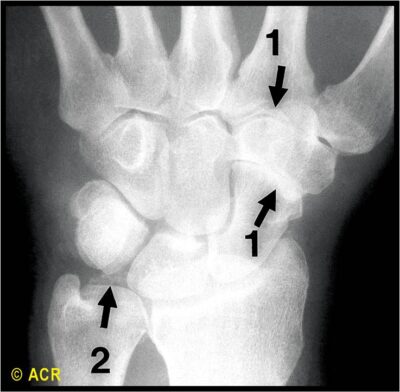
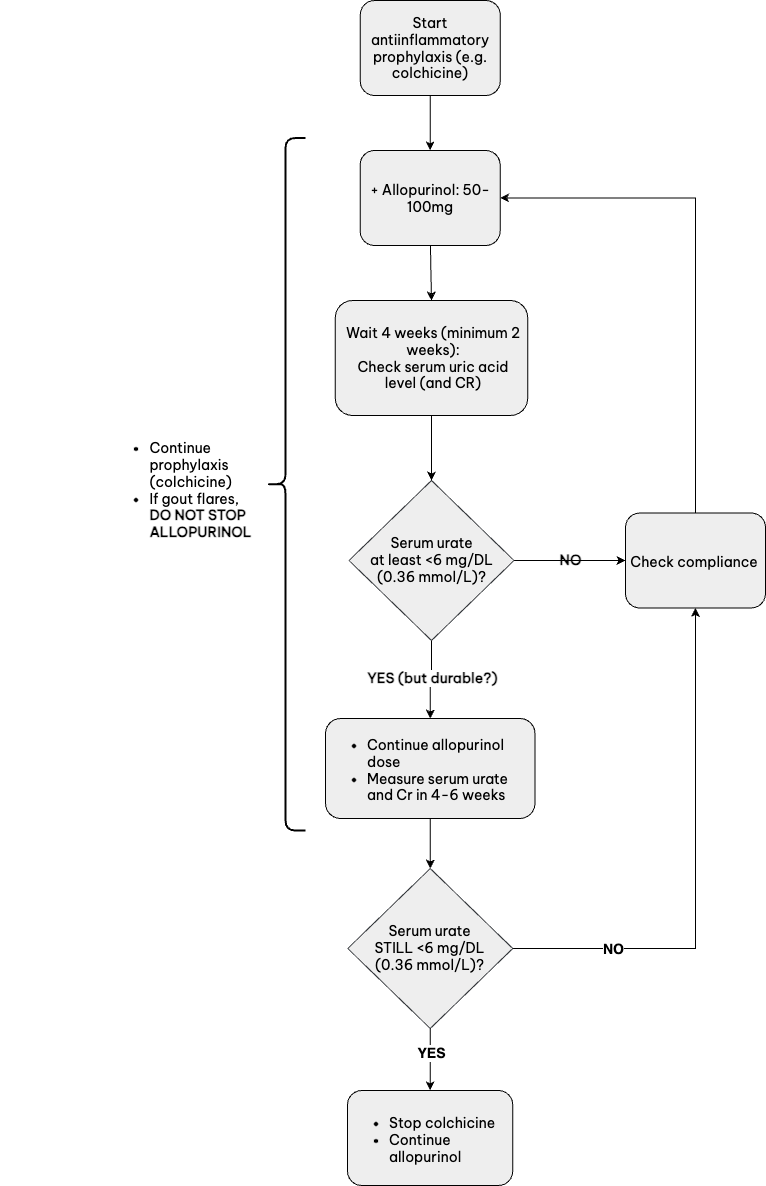
- Allopurinol (view recommended allopurinol dosing algorithm below)
- Febuxostat
- Probenecid
- Pegloticase
- Prophylaxis against flare when urate-lowering therapy started or escalated
Recommended Allopurinol Dosing Algorithm
Gout
- Target serum uric acid <6 mg/dL to reduce frequency of flares. A lower target may be needed in resistant cases or to resolve tophaceous deposits.
Pseudogout
- Complication includes spinal involvement of C1/C2 joint:
- Called “Crowned Dens Syndrome”
- Can mimic meningitis
BCP Arthritis
- Surgical or arthroscopic debridement of large symptomatic or recurrent calcific deposits may be necessary.
Clinical Presentation & Diagnostic Workup
Crystalline Arthritis
- Mimics infection:
- High CRP
- High WBC in joint fluid
Gout
- Almost never diagnosis for premenopausal female
- Podagra: Sufficient for gout dx
Note: Osteoarthritis (OA) has noninflammatory 1st MTP pain - Gout flare most common risk factors: beer, other alcohol, red meat, seafood, kidney injury/fluid shifts
CPPD
- MCP 2/3 involvement can mimic seronegative rheumatoid arthritis
BCP
- Shoulder tendons/bursa most common, AKA “Milwaukee shoulder”
Treatment
- Colchicine:
- Works best when started within first 24-48 hrs of flare onset
- Metabolized by CYP3A4 – risk of toxicity with CYP3A4 inhibitors (macrolides, antifungals, grapefruit juice)
- After steroid taper for acute treatment, watch for rebound arthritis – slow down taper
- Allopurinol can rarely cause severe cutaneous adverse reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome