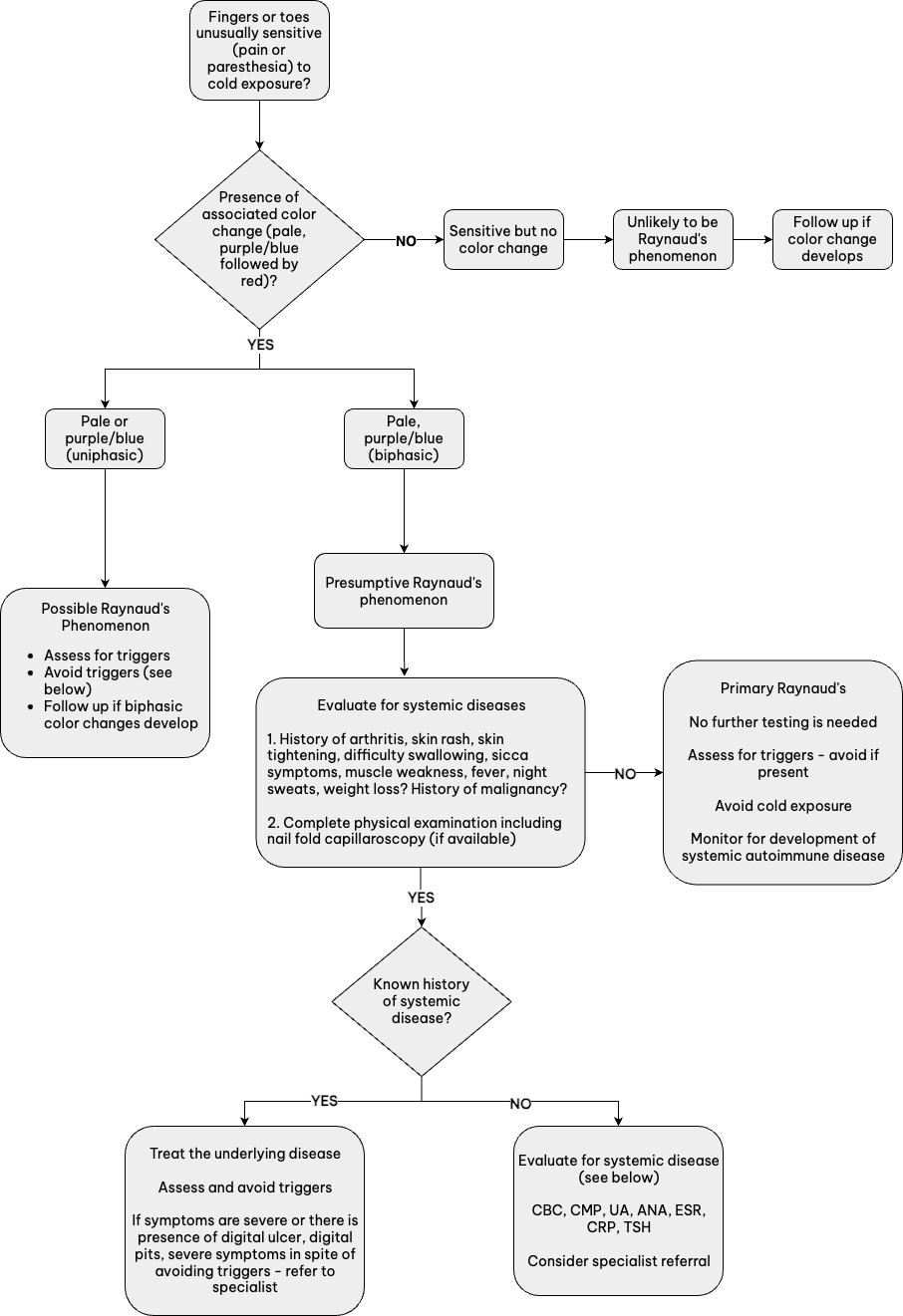
About Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Raynaud’s phenomenon is defined as vascular spasms in extremities leading to triphasic color changes: white (due to ischemia), blue (due to cyanosis), then red (due to reperfusion). Fingers and toes are most commonly affected; however, sometimes other areas are involved (tip of nose, lips, earlobes).
Raynaud’s is classified into two different types:
- Primary Raynaud’s: occurs on its own without connection to another disease or condition.
- Secondary Raynaud’s: occurs as a symptom associated with an underlying condition, medication, or lifestyle factor.
- Vasculopathy:
- Occlusive peripheral vascular disease
- Livedo reticularis
- Chilblains
- Thromboangiitis obliterans
- Thromboembolic disease
- Acute idiopathic blue finger (paroxysmal finger hematoma)
- Acrocyanosis
- External blood vessel compression
- Complex regional pain syndrome
- Erythromelalgia
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Excessive cold sensitivity
- Smoking
- Caffeine
- Emotional stress
- Drugs: Migraine medications (serotonin agonist), sympathomimetics, beta-blockers, ADHD medications, chemotherapeutics, others (interferons, cocaine, polyvinyl chloride)
- Systemic sclerosis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Myositis
- Mixed connective tissue disease
- Sjogren’s disease
- Cryoglobulinemia
- Vasculitis
- Cold agglutinin disease
- Paraneoplastic syndrome