About Systemic Sclerosis
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a systemic autoimmune disease with characteristic interstitial, vascular fibrosis in the skin +/- internal organs.
Key Subtypes
Limited SSc (lSSc)
- Skin tightening distal to elbow/wrist, knee/ankle
- Think “CREST” syndrome:
- Calcinosis
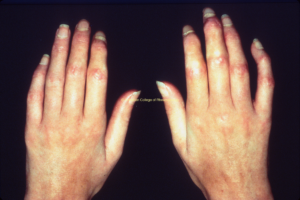
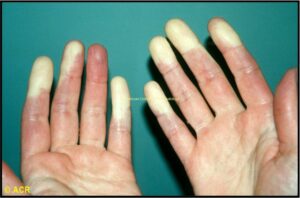
- Raynaud’s (>90%) (view image)
- Esophageal reflux
- Sclerodactyly (view image)
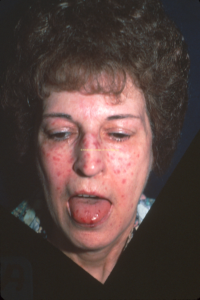
- Telangiectasia (view image)
- Centromere antibody+
- Complication of concern: pulmonary hypertension
- Rare association: primary biliary cholangitis
- Can still have lung disease
Diffuse SSc (dSSc)
- Skin tightening proximal to elbows and thighs and can involve trunk
- Tendon friction rubs (palpable crepitus over tendons)
- Can see anti-Scl-70 (anti-topoisomerase) often with nucleolar ANA pattern
- Association with scleroderma renal crisis with RNA polymerase III antibody
- Interstitial lung disease, pulmonary fibrosis
SSc Sine Scleroderma
- SSc antibodies
- Internal organ involvement
- No skin tightening
Localized Scleroderma (skin limited)
- Morphea
- Linear scleroderma
Evaluation Guide
- Concern for organ involvement other than skin?
- Pattern of skin disease? Diffuse or limited to extremities? (Skin tightening proximal or distal to elbow/wrist, knee/ankle? Does it involve the trunk (diffuse SSc)?
- What internal organs involved?
- Raynaud’s (view image)
- Gastrointestinal tract
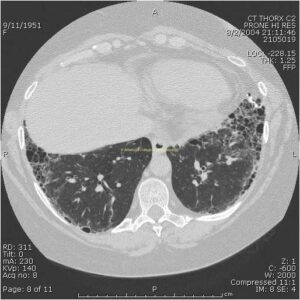
- Lung: ILD: PFTs, high-res CT w/o contrast (view image), chest x-ray
- Pulmonary artery (pHTN): DLCO, TTE
- Renal: scleroderma renal crisis (SRC)
- Heart: cardiac fibrosis
- Musculoskeletal: myositis, arthritis
Basic Labs
- CBC with differential (anemia of chronic disease, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia if scleroderma renal crisis)
- CMP
- ESR/CRP
- Urinalysis
SSc Serologies
- ANA (80-90%)
- SCL-70/topoisomerase: diffuse SSc
- Centromere: limited SSc
- RNA polymerase III: SRC
- Scleredema (DM2)
- Scleromyxedema (MGUS)
- Paraneoplastic
- POEMS
- Chronic graft vs. host disease
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
- Eosinophilic fasciitis
- Amyloidosis
- Drug exposure (e.g., bleomycin)
- Environmental exposure (organic solvents, etc.)
- Highly recommend rheumatology referral before initiating treatment, as many components of SSc management require multi-disciplinary care and collaboration
- Treatment is based on extent of skin disease, organs involved, severity of disease
- Avoid prednisone ≥15 mg/day (associated with scleroderma renal crisis [SRC])
- Skin fibrosis:
- Mycophenolate; can slow progression
- Methotrexate
- Collaboration with dermatology
- Raynaud’s:
- Avoid triggers (cold, smoking, stress/anxiety)
- Calcium channel blockers, topical nitroglycerin, PDE-5 inhibitors (do not combine with nitroglycerin), SSRI (fluoxetine). If refractory or severe digital ischemia, IV prostaglandin (hospitalization required)
- Arthritis:
- DMARDS: hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate
- DMARDS: hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate
- ILD:
- Mycophenolate: less toxic than cyclophosphamide
- Cyclophosphamide
- Anti-fibrotics (nintedanib)
- Tocilizumab
- SRC: ACEi and collaboration with nephrology
- pHTN treatment in collaboration with pulmonology
- GERD/dysphagia: H2 blockers, PPI and collaboration with gastroenterology
- Manage BP to decrease risk of renal crisis
- SRC is an emergency! Give ACEi (captopril) without delay. However, prophylactic ACE inhibitor is not suggested as it can lead to harder-to-detect SRC; recommend avoiding ACEi for antihypertensive therapy if alternate options available.
- Every visit, monitor for symptoms of extra-derm disease:
- ILD (view image)
- pHTN
- Renal crisis (20% of dSSc, 5% of lSSc)
- Myopericarditis
- CBC, CMP, U/A: monitored for drug toxicity and disease activity
- Follow-up testing for organs of concern: PFTs with DLCO, TTE, CT chest, GI scope
- Cancer screening
General
- If there is no Raynaud’s and/or ANA is negative, SSc is rarely the diagnosis!
- Scleroderma renal crisis (SRC): usually with diffuse SSc and early on in disease (first 5 yrs) – presents with sudden increase of BP
Evaluation
- Lab abnormalities in SRC: increase in serum creatinine, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (MAHA)
- Antibodies to RNA polymerase III important to identify risk for SRC
Treatment & Monitoring
- ACEi should not be given prophylactically to prevent scleroderma renal crisis (SRC), but it is the gold standard treatment for SRC.
- Do not delay giving ACEi (captopril)
- Needs to be treated in hospital
- Avoid high dose glucocorticoids due to their associated increased risk of renal crisis
- Steroids do not decrease skin tightening
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD) carries high mortality and is seen more with anti-Scl-70
- Pulmonary HTN is significant cause of mortality for limited SSc
- Close monitoring of BPs and serial TTEs and PFTs are key